Custom Fields
- Overview
- Creating Field Groups
- Using Fields in Document Types
- Accessing Fields in Templates
- Field Configuration Options
- Field Type Configuration and Usage
- Field Type Attributes
- Creating Custom Field Types
- Field Value Converters
- Macros
- Best Practices
Note: This document depends on the Filament Field Group. Field types may not update automatically; for missing or updated field references, please consult that repository.
Additional Note: The following field types are provided as custom fields by the InspireCMS plugin:
- Repeater
- Tags
- Rich Editor
- Markdown Editor
- Content Picker
- Media Picker
- Icon Picker
All other field types listed in this document are sourced from the Filament Field Group package.
Overview
InspireCMS offers a wide range of field types for different content needs:
| Field Type | Description | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
| Text | Single-line text input | Titles, headings, names |
| Text Area | Multi-line text input | Descriptions, short paragraphs |
| Rich Editor | WYSIWYG HTML editor | Formatted content bodies |
| Markdown Editor | Markdown text editor | Technical documentation |
| Validated email input | Contact information | |
| URL | Validated URL input | External links |
| Number | Numeric input | Quantities, ratings |
| Select | Dropdown selection | Categories, statuses |
| Toggle | On/off switch | Feature flags, visibility settings |
| Radio | Radio button group | Mutually exclusive options |
| File | File upload | Documents, downloads |
| Image | Image upload | Photos, illustrations |
| Color Picker | Color selection tool | Theme colors, text highlights |
| DateTime Picker | Date/time selector | Publication dates, event times |
| Content Picker | Reference other content | Related articles, products |
| Media Picker | Select from media library | Gallery images, videos |
| Icon Picker | Icon selection tool | Heroicon identifiers |
| Repeater | Group of repeatable fields | Team members, features list |
| Tags | Multiple keyword input | Blog tags, product attributes |
Creating Field Groups
Field groups organize related fields together. To create a field group:
-
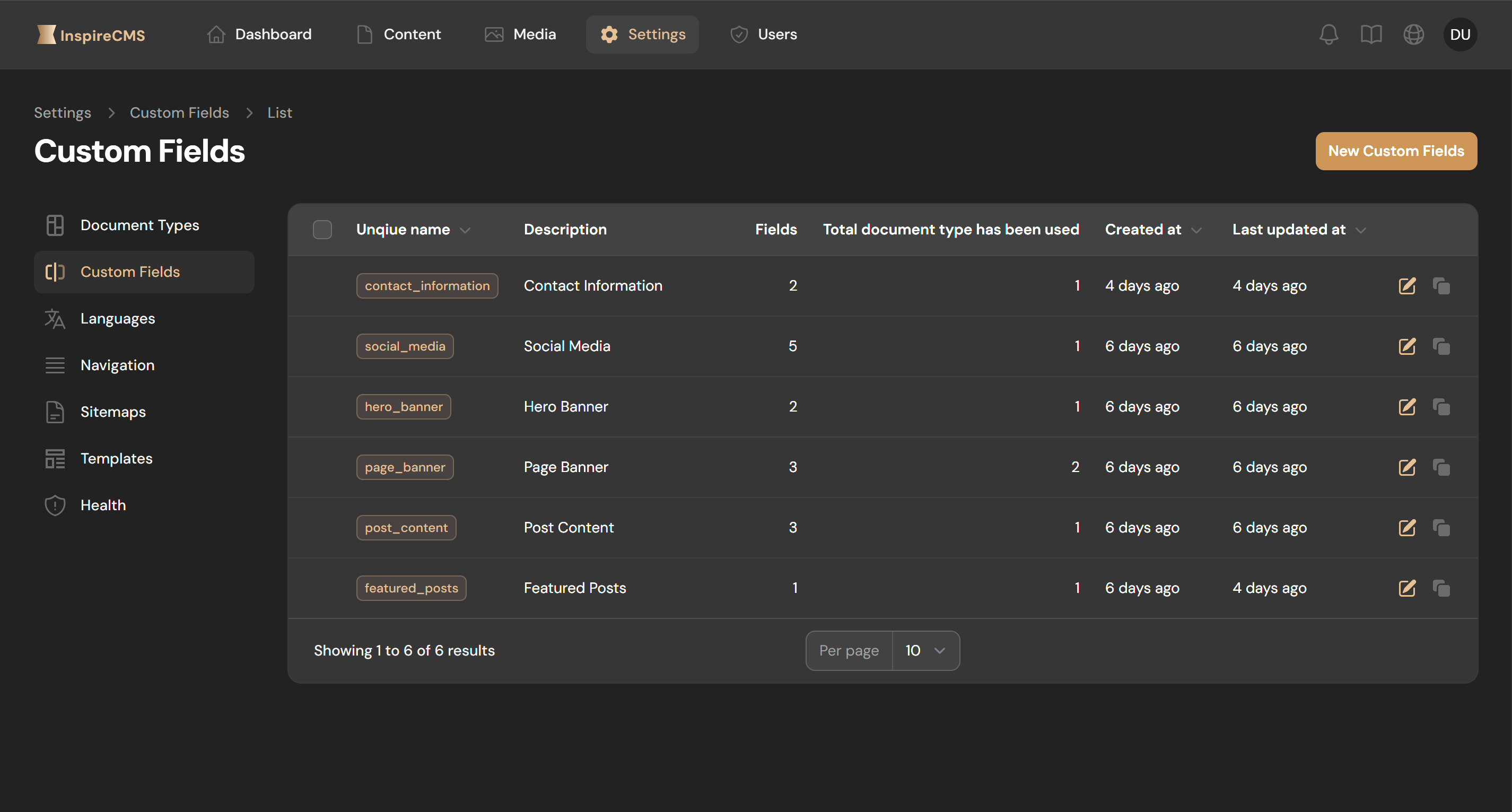
Navigate to Settings > Custom Fields in the admin panel
-
Click New Custom Fields
-
Add fields to the group using the form
-
Enter a name and slug for your field group
Using Fields in Document Types
After creating field groups, associate them with document types:
-
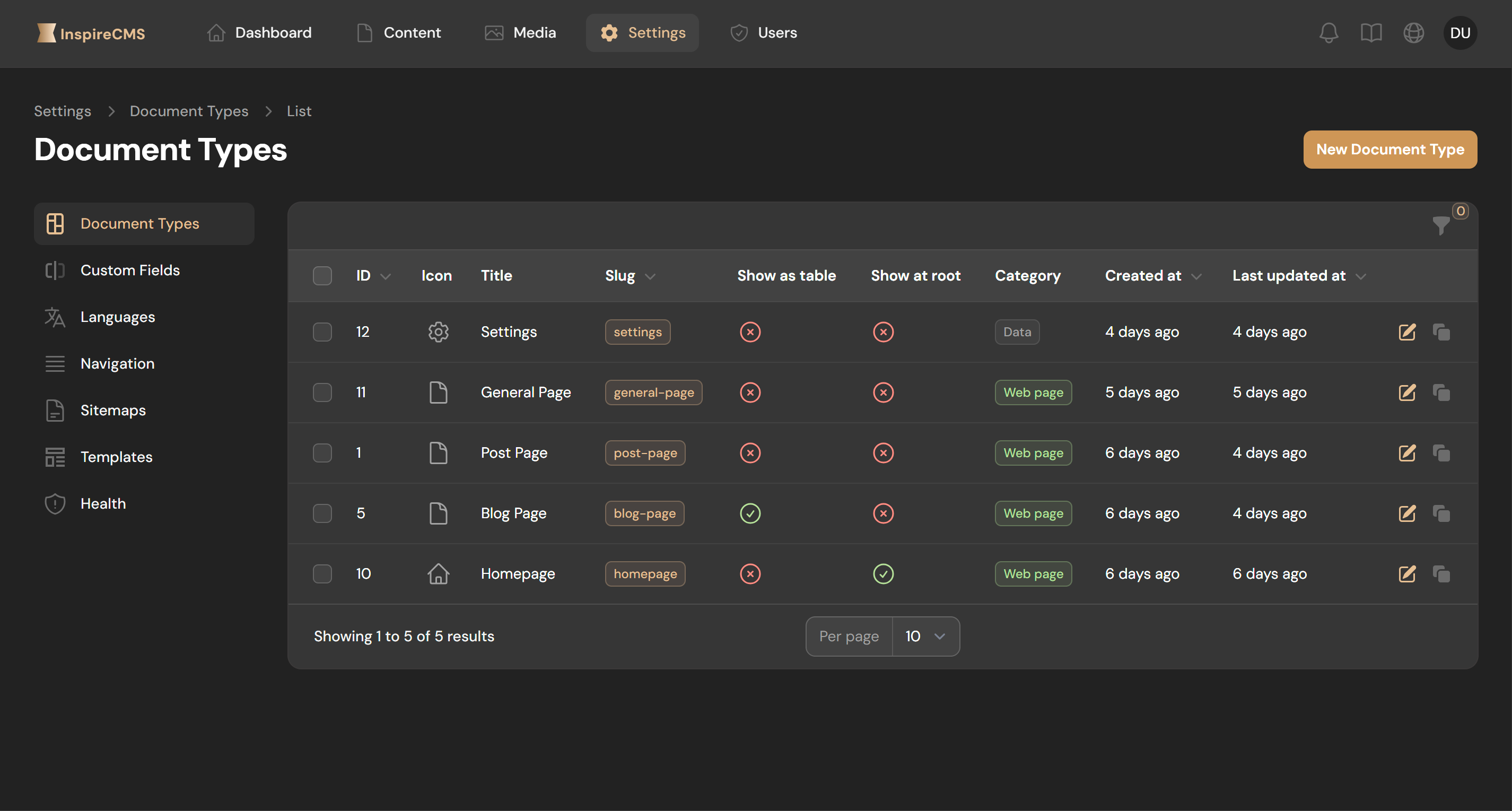
Navigate to Settings > Document Types
-
Create or edit a document type
-
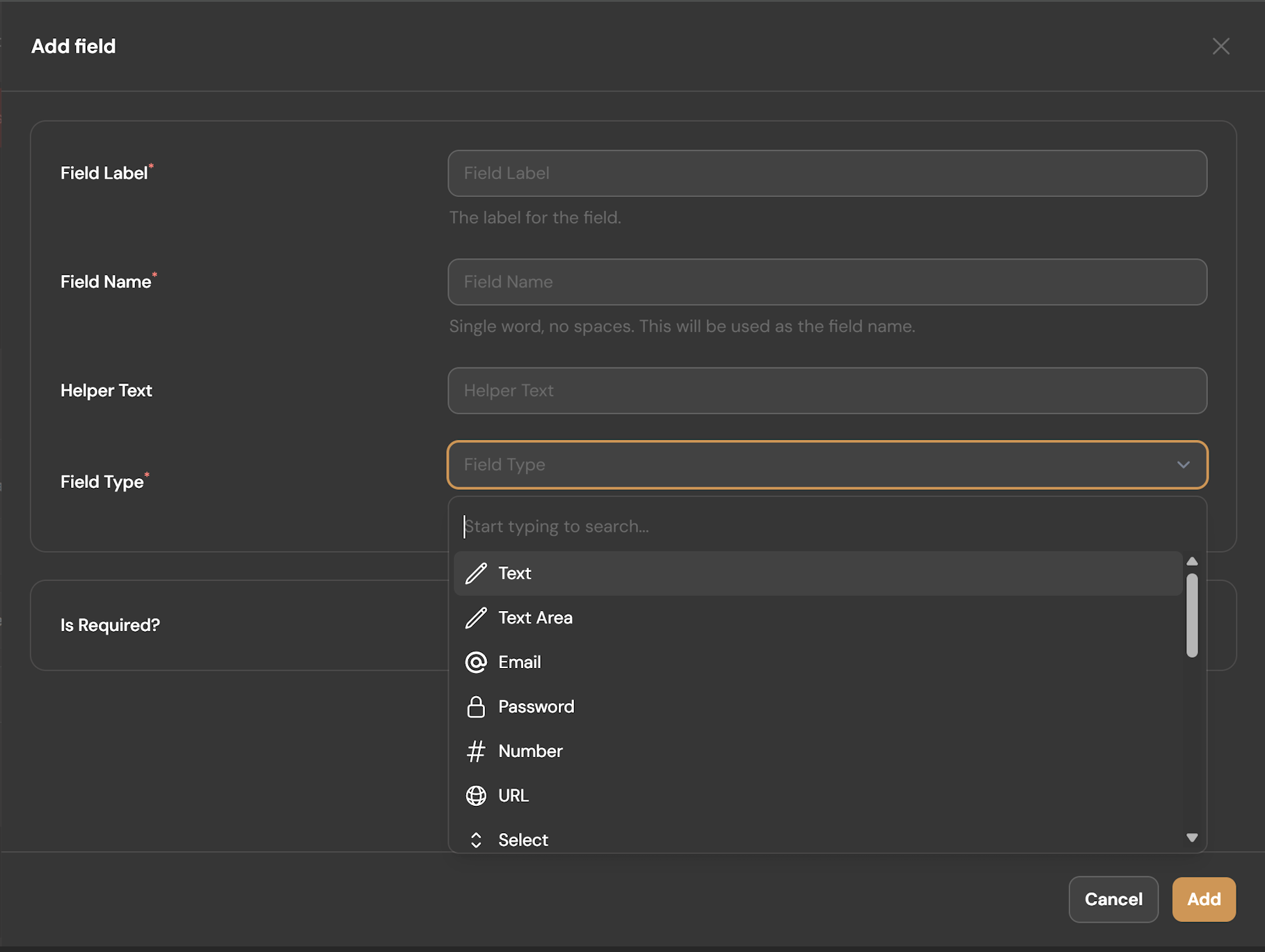
Under "Structures," select the relevant field groups
-
Save your document type
Accessing Fields in Templates
InspireCMS provides several directives to access field data in templates:
Basic Field Access
<div>@property('field_group_name', 'field_name')</div>
This outputs the field value and creates a variable $field_group_name_field_name accessible in your template.
Conditional Field Access
@propertyNotEmpty('field_group_name', 'field_name')
<h2>{{ $field_group_name_field_name }}</h2>
@endif
This checks if the field has a value before rendering content.
Accessing Arrays
@propertyArray('field_group_name', 'field_name')
@foreach($field_group_name_field_name as $item)
<div>{{ $item }}</div>
@endforeach
This is useful for repeaters, tags, and other multi-value fields.
Alternative Access Pattern
You can also access field data through the content object:
{{ $content->getPropertyGroup('field_group_name')->getPropertyData('field_name')->getValue() }}
Field Configuration Options
Each field type has specific configuration options, but most share these common settings:
- Label: The display name shown to content editors
- Name: The technical identifier used in templates
- Helper Text: Additional guidance shown below the field
- Required: Whether the field must be filled
- Translatable: Whether the field should be multilingual
Field Type Configuration and Usage
Text
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Default Value: The initial value of the field.
- Placeholder: Text displayed inside the field when empty.
- Prefix Label: Text displayed before the field.
- Suffix Label: Text displayed after the field.
- Rule: Validation rules for the field.
- Length: The exact length of the input.
- Max Length: The maximum allowed length of the input.
- Min Length: The minimum required length of the input.
Template Usage
@property('hero', 'title')
Text Area
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Rows: The number of visible rows in the text area.
- Default Value: The initial value of the field.
- Placeholder: Text displayed inside the field when empty.
- Rule: Validation rules for the field.
Template Usage
@property('intro', 'text')
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Default Value: The initial value of the field.
- Placeholder: Text displayed inside the field when empty.
- Prefix Label: Text displayed before the field.
- Suffix Label: Text displayed after the field.
- Rule: Validation rules for the field.
Template Usage
@property('contact', 'email')
Password
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Placeholder: Text displayed inside the field when empty.
- Rule: Validation rules for the field.
Template Usage
@property('user', 'password')
Number
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Default Value: The initial value of the field.
- Placeholder: Text displayed inside the field when empty.
- Prefix Label: Text displayed before the field.
- Suffix Label: Text displayed after the field.
- Rule: Validation rules for the field.
- Min Value: The minimum allowed value.
- Max Value: The maximum allowed value.
Template Usage
@property('event', 'max_ppl')
URL
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Default Value: The initial value of the field.
- Placeholder: Text displayed inside the field when empty.
- Prefix Label: Text displayed before the field.
- Suffix Label: Text displayed after the field.
- Rule: Validation rules for the field.
Template Usage
@property('contact', 'facebook')
Select
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Options: The predefined choices available in the dropdown.
- Multiple: Whether multiple selections are allowed.
- Default Value: The initial value of the field.
- Rule: Validation rules for the field.
Template Usage
Multiple is false:
@property('event', 'type')Multiple is true:
@propertyArray('event', 'types') {{ implode(', ', $event_types ?? []) }}
Toggle
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
Template Usage
@if ($content?->getPropertyGroup('event')?->getPropertyData('active')?->getValue() ?? false) @endif
Radio
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Options: The predefined choices available for selection.
- Default Value: The initial value of the field.
Template Usage
@property('user', 'gender')
File
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Disk: The storage disk where files are saved.
- Directory: The directory path within the disk.
- Visibility: The visibility of the uploaded files.
- Multiple: Whether multiple files can be uploaded.
- Rule: Validation rules for the field.
- Accepted File Types: The allowed file types for upload.
- Min File: The minimum number of files required.
- Max File: The maximum number of files allowed.
- Min Size: The minimum file size allowed.
- Max Size: The maximum file size allowed.
Template Usage
@propertyArray('event', 'docs') @foreach ($event_docs ?? [] as $doc) <a href="{{ \Storage::disk($doc->disk)->url(implode('/', array_filter([$doc->directory, $doc->path], 'filled'))) }}">Doc</a> @endforeachOr
@propertyArray('event', 'docs') @foreach ($event_docs ?? [] as $doc) <a href="{{ $doc }}">Doc</a> @endforeach
Image
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Disk: The storage disk where images are saved.
- Directory: The directory path within the disk.
- Visibility: The visibility of the uploaded images.
- Multiple: Whether multiple images can be uploaded.
- Rule: Validation rules for the field.
- Accepted File Types: The allowed file types for upload.
- Min File: The minimum number of images required.
- Max File: The maximum number of images allowed.
- Min Size: The minimum image size allowed.
- Max Size: The maximum image size allowed.
Template Usage
@propertyArray('event', 'images') @foreach ($event_images ?? [] as $img) <img src="{{ \Storage::disk($img->disk)->url(implode('/', array_filter([$img->directory, $img->path], 'filled'))) }}" alt="Event Image"> @endforeachOr
@propertyArray('event', 'images') @foreach ($event_images ?? [] as $img) <img src="{{ $img }}" alt="Event Image"> @endforeach
Color Picker
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Default Value: The initial value of the field.
Template Usage
@propertyNotEmpty('user', 'fav_color') <p style="color: {{ $user_fav_color }}">$user_fav_color</p> @endif
DateTime Picker
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Default Value: The initial value of the field.
- Placeholder: Text displayed inside the field when empty.
- Prefix Label: Text displayed before the field.
- Suffix Label: Text displayed after the field.
- Has Time: Whether the field includes time selection.
- Has Date: Whether the field includes date selection.
- Rule: Validation rules for the field.
- Format: The format of the date/time value.
Template Usage
@propertyNotEmpty('event', 'date') <p>Year: {{ $event_date?->format('Y') }}</p> @endif
Content Picker
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Types: The types of media files allowed.
- Min: The minimum number of items required.
- Max: The maximum number of items allowed.
Template Usage
@propertyArray('hero', 'image_slider') @foreach ($hero_image_slider ?? [] as $item) <div class="swiper-slide"> <img src="{{ $item?->getUrl() }}" alt="Slide {{ $loop->iteration }}"> <p>{{ $item?->description }}</p> </div> @endforeach
Media Picker
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Types: The types of media files allowed.
- Min: The minimum number of items required.
- Max: The maximum number of items allowed.
Template Usage
@propertyArray('hero', 'image_slider') @foreach ($hero_image_slider ?? [] as $item) <div class="swiper-slide"> <img src="{{ $item?->getUrl() }}" alt="Slide {{ $loop->iteration }}"> <p>{{ $item?->description }}</p> </div> @endforeach
Icon Picker
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- ColumnsLayout: Controls how many columns the icons are displayed in the selection interface.
Template Usage
@propertyNotEmpty('section', 'icon') @svg($section_icon, ['class'=>'h-5 w-5']) @endif
Repeater
Configuration Options
- Fields: The sub-fields included in the repeater.
- Collapsible: Whether the repeater sections can be collapsed.
- Cloneable: Whether the repeater sections can be cloned.
- ColumnsLayout: Controls how many columns the repeater items are displayed in.
Template Usage
@propertyArray('document_content', 'sections') @foreach ($document_content_sections ?? [] as $item) <section> <h1>{{ $item->getPropertyData('title')?->getValue() }}</h1> <p>{{ $item->getPropertyData('description')?->getValue() }}</p> {{ $item->getPropertyData('content')?->getValue() ?? '' }} </section> @endforeach
Tags
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Prefix Label: Text displayed before the field.
- Suffix Label: Text displayed after the field.
- Prefix: Text added before each tag.
- Suffix: Text added after each tag.
- Separator: The character used to separate tags.
- Suggestions: Predefined suggestions for tags.
- Reorderable: Whether tags can be reordered.
- Color: The color of the tags.
- Rule: Validation rules for the field.
Template Usage
@propertyArray('event', 'categories') <p>{{ implode(' | ', $event_categories ?? []) }}</p>
Rich Editor
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Toolbar Buttons: The buttons available in the editor toolbar.
- Disk: The storage disk where files are saved.
- Directory: The directory path within the disk.
- Visibility: The visibility of the uploaded files.
Template Usage
@property('event', 'content')
Markdown Editor
Configuration Options
- Translatable: Whether the field supports multiple languages.
- Toolbar Buttons: The buttons available in the editor toolbar.
- Disk: The storage disk where files are saved.
- Directory: The directory path within the disk.
- Visibility: The visibility of the uploaded files.
Template Usage
@property('document', 'content')
Field Type Attributes
Field types in InspireCMS are defined by a set of attributes that control their behavior, storage, and presentation. These attributes ensure seamless integration with the system.
Core Attributes
- ConfigName: A unique identifier for the field type configuration. This is used internally to load the appropriate configuration class for each field type.
- DbType: Specifies how the field's data is stored in the database, including the data type and structure.
- FormComponent: Defines the Filament form component used to render the field in the admin interface, controlling the user interface for content editors.
Additional Attributes
- Translatable: Indicates whether the field supports multilingual content. If enabled, the system stores separate values for each configured language.
- Converter: A class responsible for transforming data between its raw database format and the format used in templates. Converters handle data processing during both saving and retrieval.
Example Configuration
For a simple text field:
- ConfigName:
text - DbType:
string - FormComponent:
TextInput::class - Translatable:
true - Converter:
TextConverter::class
Creating Custom Field Types
InspireCMS allows you to create custom field types for specialized needs:
- Create a field type configuration class
- Register the field type
Example configuration class:
<?php
use SolutionForest\FilamentFieldGroup\FieldTypes\Configs\Attributes\ConfigName;
use SolutionForest\FilamentFieldGroup\FieldTypes\Configs\Attributes\DbType;
use SolutionForest\FilamentFieldGroup\FieldTypes\Configs\Attributes\FormComponent;
use SolutionForest\FilamentFieldGroup\FieldTypes\Configs\Contracts\FieldTypeConfig;
use SolutionForest\FilamentFieldGroup\FieldTypes\Configs\FieldTypeBaseConfig;
use SolutionForest\InspireCms\Fields\Configs\Attributes\Translatable;
#[ConfigName('my_custom_field', 'My Custom Field', 'Custom Fields', 'heroicon-o-star')]
#[FormComponent(\Filament\Forms\Components\TextInput::class)]
#[DbType('mysql', 'text')]
#[Translatable(true)]
class MyCustomFieldConfig extends FieldTypeBaseConfig implements FieldTypeConfig
{
// Field configuration
}
Option 1: Register in service provider:
app/Providers/AppServiceProvider.php
<?php
use SolutionForest\FilamentFieldGroup\Facades\FilamentFieldGroup;
public function boot()
{
FilamentFieldGroup::fieldTypeConfigs([
MyCustomFieldConfig::class,
]);
}
Options 2: Register in the Configuration File
Alternatively, you can register the custom field type in the custom_fields.extra_config array of the config/inspirecms.php file. This approach centralizes the configuration and is easier to manage for multiple custom field types.
config/inspirecms.php
// ...existing code...
'custom_fields' => [
'extra_config' => [
CustomFieldConfig::class, // Add your custom field configuration here
// ...existing field configurations...
],
],
Field Value Converters
Field type converters are responsible for transforming data between the raw format stored in the database and the format used in templates. They play a crucial role in ensuring data is properly processed, validated, and formatted throughout the content lifecycle.
Purpose of Converters
- Data Transformation: Convert between database storage format and usable application format
- Type Casting: Ensure data is of the correct PHP type when used in templates
- Value Preparation: Handle any necessary pre-processing before storage or display
Built-in Converters
InspireCMS includes several built-in converters for common field types:
| Converter | Purpose |
|---|---|
| DefaultConverter | Basic conversion for simple field types like text and numbers |
| DateTimeConverter | Converts between string dates and DateTime objects |
| ContentPickerConverter | Transforms content references into usable content objects |
| FileConverter | Handles file path conversions and URL generation |
| MarkdownConverter | Processes markdown text into HTML for display |
| MediaPickerConverter | Manages media asset conversions and metadata |
| RepeaterConverter | Processes nested field groups within repeater fields |
| RichEditorConverter | Handles HTML content sanitization and processing |
Creating Custom Converters
Value converters transform field data between storage format and display format:
<?php
use SolutionForest\InspireCms\Fields\Converters\BaseConverter;
class MyCustomConverter extends BaseConverter
{
public function toDisplayValue(mixed $sourceValue, ?string $locale, ?string $fallbackLocale)
{
// Transform the value for display
return $this->processValue($sourceValue);
}
}
Then, apply your converter to a field type using the Converter attribute:
use SolutionForest\FilamentFieldGroup\FieldTypes\Configs\Attributes\ConfigName;
use SolutionForest\FilamentFieldGroup\FieldTypes\Configs\Attributes\DbType;
use SolutionForest\FilamentFieldGroup\FieldTypes\Configs\Attributes\FormComponent;
use SolutionForest\FilamentFieldGroup\FieldTypes\Configs\Contracts\FieldTypeConfig;
use SolutionForest\FilamentFieldGroup\FieldTypes\Configs\FieldTypeBaseConfig;
use SolutionForest\InspireCms\Fields\Configs\Attributes\Converter;
use SolutionForest\InspireCms\Fields\Configs\Attributes\Translatable;
#[ConfigName('customField', 'Custom Field', 'Custom', 'heroicon-o-tag')]
#[FormComponent(\Filament\Forms\Components\TextInput::class)]
#[DbType('mysql', 'text')]
#[DbType('sqlite', 'text')]
#[Converter(\App\Support\Converters\CustomConverter::class)]
#[Translatable(true)]
class CustomFieldConfig extends FieldTypeBaseConfig implements FieldTypeConfig
{
// Field configuration implementation
}
Configuring Converters
You can customize the behavior of built-in converters by using their configuration methods. Configure converters in your service provider's boot method:
app/Providers/AppServiceProvider.php
use SolutionForest\InspireCms\Fields\Converters\MarkdownConverter;
use League\CommonMark\Extension\Attributes\AttributesExtension;
use League\CommonMark\Extension\Table\TableExtension;
public function boot(): void
{
MarkdownConverter::configureUsing(function (MarkdownConverter $converter) {
// Set CommonMark configuration options
$converter->setConfigs([]);
// Add CommonMark extensions
$converter->setExtensions([
new AttributesExtension(),
]);
});
}
Each converter type may have its own configuration methods:
MarkdownConverter
The MarkdownConverter handles parsing and rendering of Markdown content using the PHP League's CommonMark library. You can customize the parser with various extensions and configuration options:
use SolutionForest\InspireCms\Fields\Converters\MarkdownConverter;
MarkdownConverter::configureUsing(function (MarkdownConverter $converter) {
// Set CommonMark configuration options
$converter->setConfigs([
'allow_unsafe_links' => false,
'html_input' => 'strip',
'max_nesting_level' => 100,
'renderer' => [
'soft_break' => "<br>\n",
],
]);
// Add CommonMark extensions
$converter->setExtensions([
new AttributesExtension(),
new TableExtension(),
]);
});
For more information, see:
Macros
The Field Type system supports macros, allowing you to extend functionality without creating full custom field types. This approach is useful for adding small enhancements or modifications to existing field types.
You can use the mixin method to add multiple macros at once:
use SolutionForest\FilamentFieldGroup\FieldTypes\Configs\FieldTypeBaseConfig;
// Add multiple methods via a mixin class
FieldTypeBaseConfig::mixin(new \Your\Mixins\FieldMixin);
Or add individual macros using the macro method:
use SolutionForest\FilamentFieldGroup\FieldTypes\Configs\FieldTypeBaseConfig;
// Add a single macro
FieldTypeBaseConfig::macro('addHelpText', function ($text) {
$this->helperText($text);
return $this;
});
Best Practices
- Keep field groups organized by logical function (e.g., "Banner", "Content")
- Use clear, descriptive names for fields and field groups
- Add helper text to guide content editors
- Use appropriate validation rules to ensure data quality
- Leverage translatable fields for multilingual content
- Consider the frontend display when designing field structures